How Are Sharks at SeaQuest Cared For?
Share it on:
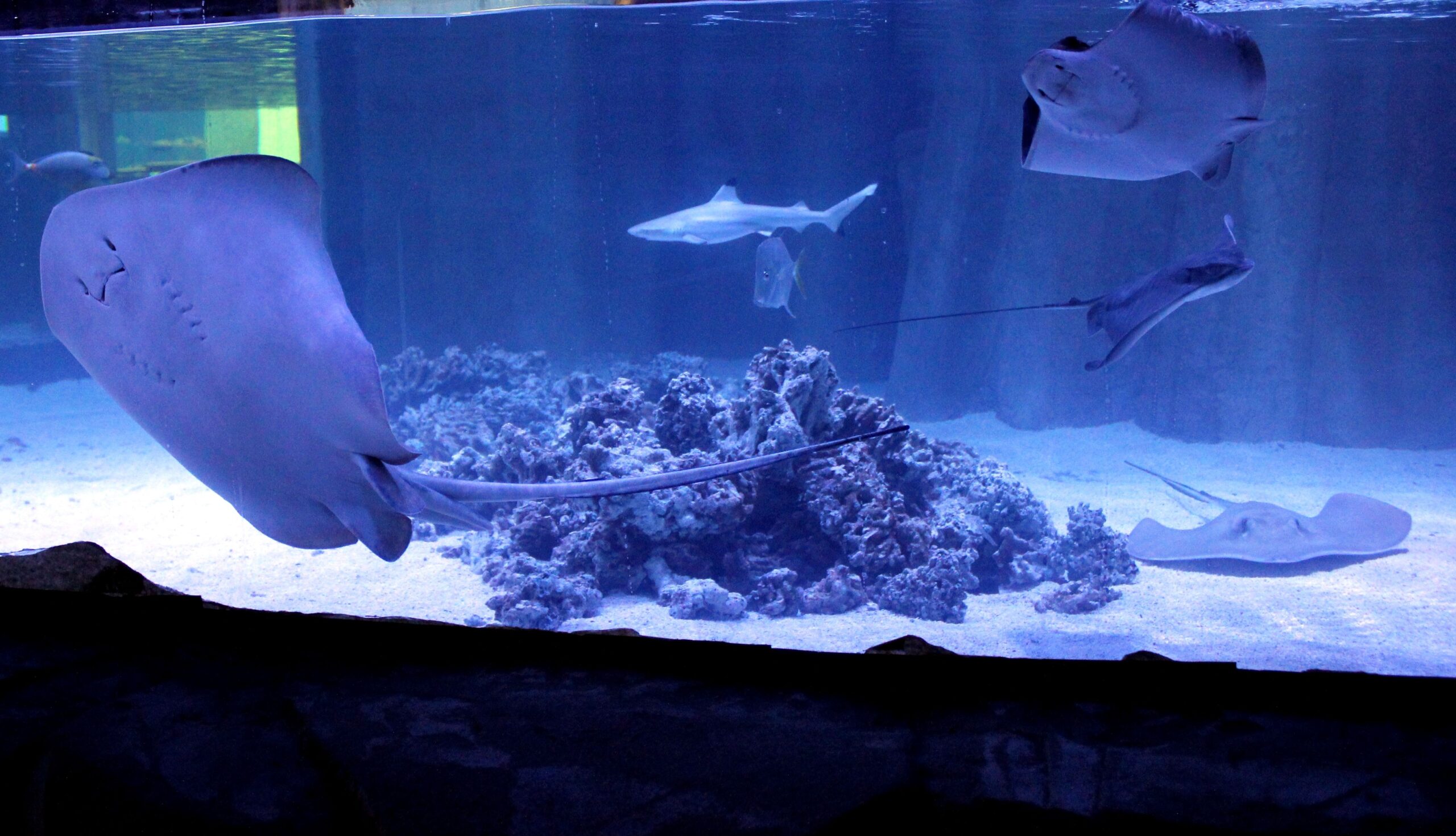

Sharks are essential to marine ecosystems worldwide. However, many sub-species face endangerment or even extinction. At SeaQuest, the environment we provide for our sharks takes top priority to accommodate their sensitive needs and help the species as a whole. Let’s look deeper at how we care for these incredible predators.
Introduction to Shark Care at SeaQuest
SeaQuest is dedicated to caring for its sharks, and we have a specific team of ambassadors dedicated to this cause. We have marine care specialists and veterinarians who specialize in elasmobranchs — a subclass of fish that encompasses sharks and other species.
These ambassadors provide a holistic approach to our sharks’ well-being, including their mental, physical, and social well-being. Our goal is to ensure their lives at SeaQuest closely resemble their lives in the wild while also advocating for the conservation of their species. This latter principle ensures that we equally prioritize the well-being of sharks under our care and sharks worldwide.
Understanding Sharks: Natural Behaviors and Habitats
To properly care for our sharks, we meticulously study their habits, behaviors, and environments in the wild. For example, the Great White Shark has never been able to survive in an aquarium due to their nomadic nature. As such, we would never inhabit them or other sharks who couldn’t thrive under our care.
What Is a Shark’s Natural Habitat?
Sharks thrive in diverse ecosystems, from the shallow, vibrant coral reefs to the mysterious depths of the open ocean and deep-sea trenches. Each species has adapted uniquely to its environment, with varying behaviors, diets, and survival strategies that reflect the characteristics of their natural habitats. For example, black tip reef sharks who live in more shallow waters around coral reefs or sandy shorelines will eat fish that live in these areas, such as reef fish or crustaceans. Meanwhile, deep-sea sharks, such as the megamouth shark, will mainly feed on zooplankton — the primary source of protein in this environment.
At SeaQuest, most of the sharks in our exhibits typically live in more shallow environments in the wild, so we can easily replicate their environment within our aquarium. This replication involves balancing the coral reefs and structural elements within our aquariums for sharks to take shelter and enough space to roam and move freely — just like they would in the wild. These spaces also fulfill their mental enrichment needs, allowing them to hide and stalk any food we disperse throughout the day.
Social Dynamics Among Sharks
Sharks exhibit a range of social behaviors that vary widely between species. Some are solitary hunters, preferring to roam the oceans alone, while others often gather in schools. Understanding these social dynamics is crucial for creating an environment that mirrors sharks’ natural social interactions and promotes their well-being.
At SeaQuest, we design our communal tanks based on the needs of both solitary and more social shark species. Our more social sharks will swim through large, interconnected tanks that mimic the open ocean conditions where these animals naturally congregate. Our more solitary species live in habitats with more structures, giving each shark its own space and reducing the chance of stress and aggression caused by forced proximity to others.
We carefully and thoughtfully introduce each new shark in a tank to achieve healthy social dynamics. We quarantine new sharks to assess their health and gradually acclimate them to the new water conditions.
Once the new sharks are deemed ready, we gradually introduce them into their communal primary habitat, often during feeding times when all sharks are more focused on food than their new tank mates. This strategy helps divert attention away from the newcomers. In every stage of this process, our internal team of marine biologists and veterinarians monitors for signs of aggression and stress. Based on these signs, they may alter the physical environment or adjust the groupings of sharks in different tanks.
Diet and Nutrition: What Do Sharks Eat?
Sharks are carnivorous, and their diets are as diverse as their environments. Depending on the species, a shark’s diet can include fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and even larger prey such as marine mammals or seabirds. Ultimately, sharks are opportunistic eaters and will eat whatever is available in their environment.
When feeding the sharks at SeaQuest, we consider the natural hunting practices of each shark in their daily feedings. For example, we will hide food within the reefs of our aquariums to encourage foraging. We will also use feeding poles to simulate live prey, moving their food through the water to encourage sharks to swim after and chase their meals, just as they would in the wild. We also provide supplements filled with essential vitamins and minerals for any nutritional deficiencies they may have. We also closely monitor them daily during and around their meals to ensure they’re not falling prey to common health issues associated with a lack of nutrients, such as wasting disease, goiter, and spinal deformities.
The Health and Well-being of Sharks at SeaQuest
In addition to the care outlined above, SeaQuest has a set standard for sharks so they can live comfortably and even thrive in our aquariums.
Ensuring Optimal Water Conditions
Sharks are attuned to the water temperature and salinity changes, which can affect their metabolic rates and overall health. For instance, tropical shark species require warmer water, while those from deeper waters need cooler temperatures. Similarly, the salinity must reflect their natural oceanic environments, which can differ between coastal and open ocean habitats. Our tanks differ based on the natural environment and the needs of its inhabitants, sharks, and fish.
To maintain this natural environment, we use advanced sensors to measure the pH, nitrogen levels, temperature, and salinity. These systems provide immediate alerts if any parameters deviate from the standard so we can address the situation without stressing or endangering the tank’s inhabitants.
We also use state-of-the-art filtration systems to remove waste products, pathogens, and chemical impurities — all of which can easily affect the physical health of sharks who rely on the water for their oxygen levels.
Beyond these automatic systems, we also manually maintain these environments. For example, we routinely clean the tanks, check and repair habitat structures, and occasionally redesign the environment to prevent boredom and stimulate natural behaviors in the sharks. This maintenance ensures the environment stays clean and provides a dynamic and exciting landscape for the sharks to explore.
Veterinary Care and Health Monitoring
As previously mentioned, our veterinary staff works to maintain the health of all our animals, including our sharks. Part of their care includes physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging technology like ultrasound—all of which screen for severe health conditions, negating the use of invasive techniques that may stress the sharks. Their care schedule also includes preventative care like vaccinations that prevent disease from spreading in our tanks.
Despite preventive efforts, accidents happen, and just like humans, our sharks may occasionally experience injuries and health conditions. To address these issues promptly, we have tailored treatment plans based on the severity and nature of the condition.
For instance, if we observe abrasions or wounds on a shark, likely from interactions with tank mates or habitat structures, immediate action is taken to treat the injuries and modify the environment as necessary to prevent future accidents. For sharks that need intensive care, we place them in quarantine areas so that they can recover without the additional stress of social dynamics in their usual habitat.
Overfishing and Shark Finning have spiked in recent years, decreasing shark populations in the world’s oceans.
Educational and Conservation Initiatives
The care SeaQuest promises sharks goes beyond those that swim through our tanks. Our care also includes those across the globe through conservation education, research, and positive human interactions.
SeaQuest’s Role in Shark Conservation
Research is crucial for understanding shark behaviors, physiology, and their role in marine ecosystems, supporting more informed conservation strategies. SeaQuest collaborates with various research institutions and universities to collect valuable data from our sharks. With this data, they’ll come across valuable conclusions and contribute to the scientific community, leading to better protective measures for sharks in the wild and captivity.
One of SeaQuest’s most impactful roles in shark conservation is through our educational programs like Shark Week. In this program, we join the cultural phenomenon that takes over the world by playing games throughout SeaQuest and educating visitors about the reality of sharks and their role in the marine ecosystem, thus dispelling any myths surrounding them.
During these programs, we also cover shark threats, such as pollution, climate change, habitat loss, and overfishing. In particular, we focus on the growing practice of shark finning. In this violent practice, poachers will catch sharks just to cut off their fins and harvest them in a multi-million dollar industry, even though it causes the shark to drown, bleed out, or die from starvation. Once visitors learn more about sharks and sympathize with them, they can become advocates for sharks and collaborate with SeaQuest on their conservation efforts.
One such effort is our habitat protection initiatives. Here, we partner with organizations that create marine protected areas (MPAs) where shark populations can thrive away from the pressures of fishing and habitat destruction. These areas provide safe havens for sharks to feed, mate, and maintain the sensitive balance of marine environments.
Promoting Responsible Interaction With Sharks
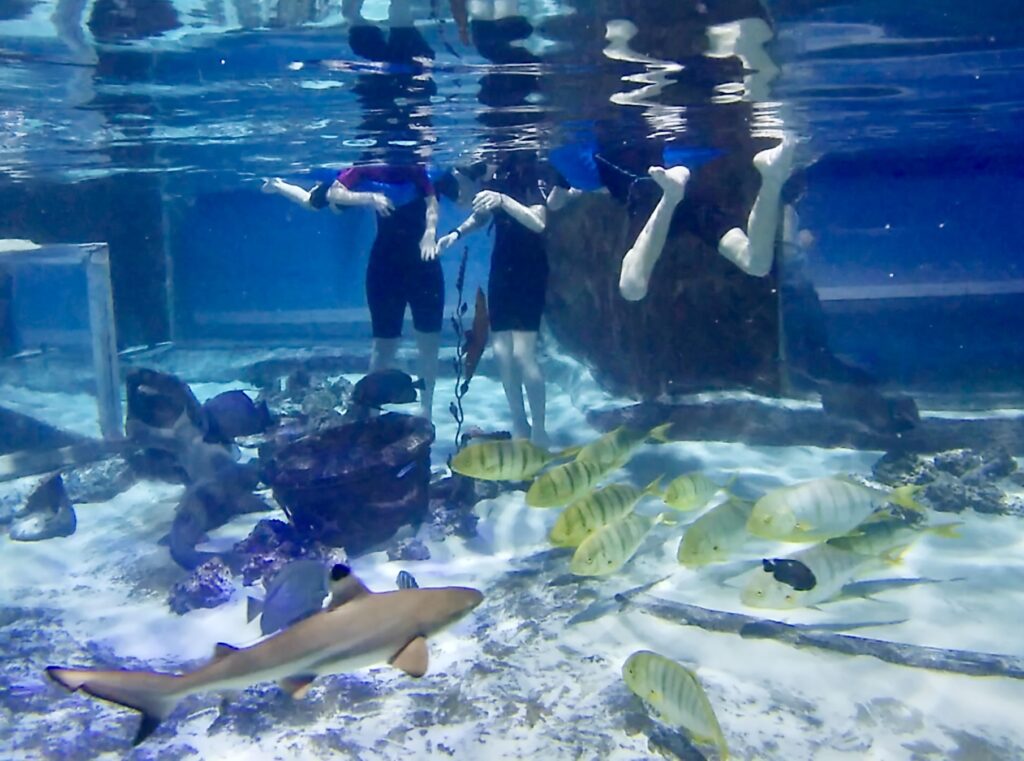
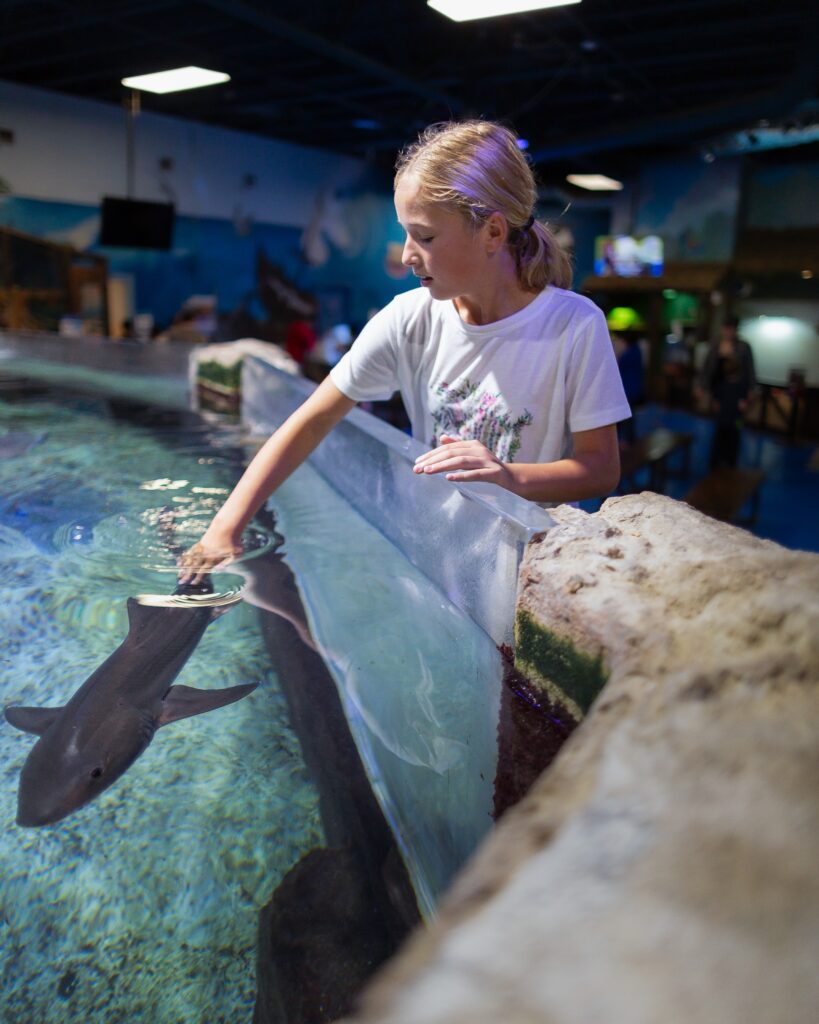
We can enhance the visitor experience by facilitating positive interactions with sharks. To have a positive experience, we will require you to follow guidelines that keep you and our sharks safe and stress-free. These guidelines include best practices for all marine welfare. For example, we ask visitors not to initiate contact with sharks but to observe their natural behavior. This is the most natural way to experience sharks — they go about living their lives while you build a striking memory.
We also ask that visitors not use flash photography, which can disorient and stress sharks, and to be quiet around the tanks to further build a calm environment. With these guidelines, visitors can focus more on the sharks and their education under strict supervision.
SeaQuest’s multifaceted approach to shark care exemplifies the profound commitment required to maintain the health and welfare of these magnificent marine creatures in a captive environment. This effort is worth it, though. By educating the public about the importance of sharks, SeaQuest inspires visitors to join in their efforts to safeguard these vital members of the marine ecosystem for future generations.







